How to Become a Cyber Security Auditor

When you study to become a cyber security auditor, you will learn the skills to work as an information security professional who assesses the computer security systems of a corporation to ensure that they are secure from cyber criminals. Information security auditors routinely produce detailed reports that discuss a system's effectiveness and suggest improvements.
We'll cover the education you need to get started in this field, the duties that await you and the skills you'll need to execute them, possible career paths, as well as your potential earnings after landing a job.
WHAT DO CYBER SECURITY AUDITORS DO?

Information security auditors carry a great load of responsibility on their shoulders. They need to ensure that a company or governmental agency is safe from criminal and terrorist behaviors.
Since most businesses and agencies keep the lion's share of their records in digital databases, these must be appropriately protected with firewalls, encryption and other security measures. These databases need to be tested periodically to ensure that they comply with the latest IT standards and practices.
They Design and Manage Audits
To ensure the security of an organization's systems, cyber auditors must design and manage audits. Depending on the size of the organization, audits might be conducted at the department level or across the entire system. The auditor's responsibility is to assess the overall structure of the organization's systems and determine the scope of the audit.
They Interpret Audit Data
Once the audit has been completed, the auditor needs to be able to interpret the resulting data. This is a highly detailed and analytical process that asks the professional to sort through endless reports with a fine-toothed comb. If, for instance, a security breach is suspected, he or she will need to scrutinize the logs to see if, when, or where an SQL database was breached or otherwise compromised. Then, the problem and its solution must be assessed and detailed.
They Write and Present Audit Reports
After analyzing the audit data, the auditor must prepare a report detailing the findings and presenting best practices for IT professionals and other staff members. If the report suggests upgrades or improvements, the auditor must provide a cost-benefit analysis to demonstrate the value of the upgrades. For example, assigning more manpower to bolster security codes will pay off by ensuring that business operations can continue safely and without costly interruptions.
STEPS TO BECOMING A CYBER SECURITY AUDITOR
To become a cyber security auditor, you will need at least a bachelor's degree, preferably in information technology, computer science or an applicable technical field. Then you will likely need roughly five years of experience in an IT department. You will always benefit from additional information security certificates, whether earned through a university or corporate training.
Step 1: Earn Your Degree in a Related Field
A degree in cyber security or a related field is essential to gain the knowledge and skills necessary to understand the technical details of an organization's security infrastructure. Cyber security auditors must be familiar with network security, cryptography, and risk management, among other things. This knowledge allows them to evaluate an organization's security posture and identify vulnerabilities.
If you're a busy professional who doesn't have the time to drive to and from a brick-and-mortar university, there are online information security degrees available in great abundance. Allowing flexibility and saving precious hours in your daily schedule.
Step 2: Gain Relevant Work Experience
Relevant work experience is crucial for an IT auditor to understand how security measures work in practice. Cyber security auditors must have experience in entry-level information security positions, such as cyber security analyst, network administrator, or information security specialist. This experience allows them to recognize common security weaknesses, identify potential risks, and develop effective strategies to protect against them.
Step 3: Obtain Certifications
Certifications provide objective validation of your knowledge and skills as a security auditor. Some of the most popular certifications for digital information auditors include Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), and Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC). These certifications demonstrate your expertise in the field and provide organizations with confidence in your abilities to conduct effective security audits.
Step 4: Develop & Hone Strong Analytical Skills
To become a cyber security auditor, you need to have a range of technical and non-technical skills. Some of the key technical skills required for this profession include knowledge of:
- network security,
- system administration,
- risk management,
- vulnerability management,
- and security testing tools.
In addition to technical skills, cyber security auditors must also possess strong non-technical skills such as:
- critical thinking,
- problem-solving,
- attention to detail,
- and communication skills.
You must be able to analyze complex information, identify risks, and provide solutions to mitigate those risks. They must also be able to communicate effectively with stakeholders at all levels of the organization, including senior executives, IT professionals, and end-users. Additionally, you must be able to stay up-to-date with the latest security threats, trends, and technologies in order to provide effective security audits and recommendations.
Step 5: NETWORK WITH OTHER IT AUDITORS
Networking with other information security specialists is vital for staying up-to-date with the latest trends, tools, and techniques in cyber security auditing. Information auditors can join professional organizations, attend conferences, and participate in online forums to connect with other professionals in the field. This networking allows them to share knowledge, ask questions, and keep pace with emerging security threats.
CYBER SECURITY AUDITOR SALARY
The work of security auditing comes under the rubric of many different job titles, but a survey of salaries in the field matches with the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics median salary for an information security analysts, who earn a median annual salary of $120,360.

ANNUAL MEDIAN SALARY OF
$120,360
Information Security Analyst
The BLS job growth projections for the field are likewise positive, as they expect the field to expand by a healthy 31.5% through 2032. However, some industries and sectors have a higher demand for cyber security auditors than others, such as the banking and finance industry, government agencies, and healthcare organizations.
In these industries, cyber security auditors are essential for ensuring compliance with industry regulations and protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. Earning your master's degree in cyber security or a similar concentration can also pave the way for career advancement and higher pay that comes with more advanced positions.
REAL-WORLD EXAMPLES OF CYBER SECURITY AUDITING
US DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY
In 2018, an audit of the US Department of Homeland Security's (DHS) computer systems identified multiple vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. The audit recommended a series of remediation steps, including patching and updating software and implementing stronger access controls. These recommendations were promptly implemented, strengthening the security posture of the DHS and mitigating the risk of potential cyber attacks.
IT AUDITING IN THE FINANCIAL SECTOR
In 2017, a cyber security audit of a major financial services company identified a number of security weaknesses in the company's IT infrastructure, including insecure passwords and weak encryption protocols. The audit report recommended several measures to improve security, including updating security software, improving security awareness training for employees, and conducting regular vulnerability assessments. The company implemented these recommendations and saw a significant reduction in the number of security incidents.
CYBER AUDITING IN HEALTHCARE
In 2019, a cyber security audit of a healthcare provider identified several vulnerabilities in the provider's electronic medical record (EMR) system, including inadequate access controls and weak encryption. The audit report recommended several steps to improve the security of the EMR system, including implementing multi-factor authentication, improving password management policies, and conducting regular penetration testing. The provider implemented these recommendations, which helped prevent potential cyber attacks and better protect patient data.
These examples demonstrate how effective information security audits can help organizations identify vulnerabilities in their IT infrastructure and implement remediation steps to mitigate risk and prevent cyber attacks.
COMMON JOB TITLES IN INFORMATION SECURITY AUDITING
If you desire to move into security auditing, there are a number of titles that require virtually the same background as this role. When you apply for these jobs, make sure that their descriptions match what you are looking for and what you are qualified to do. Furthermore, make sure that if you land the position that it will propel your career forward. Some similar titles include the following:
IT Security Auditor
Security Specialist
IA Auditor
POSSIBLE CAREER PATHS FOR IT SECURITY AUDITORS
The path of a cyber auditor has three basic tiers: entry level, IT security specialist and managerial. The following graphic outlines these levels and potential job titles for you to pursue:
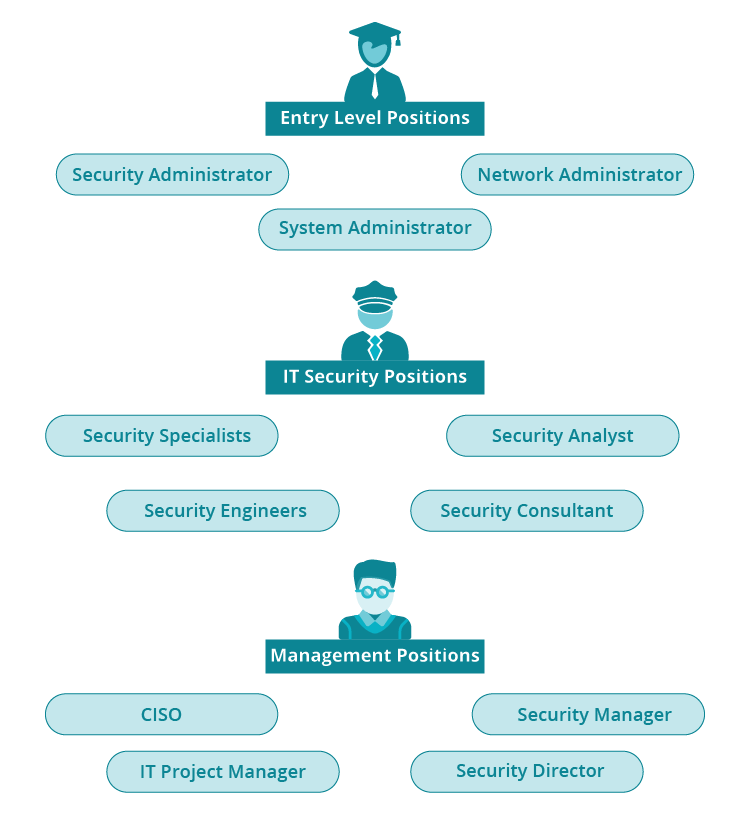
IT security auditing can lead to various opportunities in the field of cyber security. Once you become an information security auditor and choose to follow this career through, here are some possible career paths that you might pursue:
- Senior Cyber Security Auditor: Responsible for overseeing the auditing process, ensuring that audit plans are effective, and reviewing audit results. They may also be responsible for developing policies and procedures related to information security auditing.
- Cyber Security Consultant: Helps organizations improve their security posture by identifying vulnerabilities, recommending improvements, and developing security policies and procedures. A cyber auditor with experience in conducting security audits can transition into a cyber security consulting role.
- Risk Management Specialist: Leverage your knowledge of risk management to transition into a risk management specialist role. Risk management specialists help organizations identify, assess, and manage potential risks to their information assets.
- Information Security Manager: An information security manager is responsible for overseeing an organization's information security program. An IT security auditor can transition into this role by leveraging their experience in conducting security audits and identifying vulnerabilities.
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): A CISO is responsible for developing and implementing an organization's information security strategy. An IT security auditor with extensive experience in conducting security audits and risk assessments can transition into this leadership role.
- Penetration Tester: A penetration tester is responsible for identifying vulnerabilities in an organization's systems by simulating cyber-attacks. A cyber auditor with technical expertise can transition into this role.
These are just a few examples of the career paths that an IT auditor can pursue. With the rapid growth of the cyber security industry, there are many opportunities for professionals to advance their careers and make a meaningful impact in the field.
SECURITY AUDITOR VS. PENETRATION TESTER
Security auditors and penetration testers have different roles in assessing the security of an organization's IT infrastructure. Here's a breakdown of the key differences:
The Role of Cyber Security Auditors
A security auditor assesses a computer system based on established standards and makes recommendations to help the system become compliant. This assessment covers all aspects of an organization's IT structure, including potential conflicts within the system that can result in glitches and systemic difficulties. Security auditors prioritize standards that may be out of date and well-known to criminal hackers.
The Role Of Penetration Testers
A penetration tester takes on the role of a malicious hacker and attempts to hack into the system from outside, identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities. Their report provides an assessment and recommendations for added security, primarily concerning the external firewall or other security measures. However, their scope is limited, and a typical penetration test does not often take into account errors that might occur on a daily basis, such as faulty programming or other human errors.
Both roles are important in improving the overall security of an organization, but they have different areas of focus and limitations in scope. A cyber security auditor looks at the bigger picture of an organization's IT infrastructure, while a penetration tester primarily focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in external security measures. It's essential to have both roles in a corporate structure to maintain the overall integrity and health of the business.
Getting Started
As a cyber auditor you must be able to stay up-to-date with the latest security threats, trends, and technologies in order to provide effective security audits and recommendations. Getting the latest education is the first step in building the foundation for your knowledgebase, followed by field experience.
Start by using our Find Schools widget on this page and browse through our database of accredited universities who offer information security programs at all levels.
Explore Cyber Security Careers
- Becoming a Cryptographer
- Cyber Security Salaries Overview
- How to Become a Cryptanalyst
- How to Become a Cyber Security Analyst
- How to Become a Database Analyst
- How to Become a Forensics Expert
- How to Become a Network Security Analyst
- How to Become a Security Auditor
- How to Become a Security Consultant
- How to Become a Security Engineer
- How to Become a Security Software Developer
- How to Become a Security Specialist
- SOC Analyst Career Guide
